부트캠프 9일차
데이터베이스
자바로 실행한 프로그램 내 데이터들은 모두 메모리에 올려져 사용된다. 즉, 프로그램이 종료되면 모두 소멸된다는 것인데 이 데이터들이 소멸되지 않고 계속 보관되어 있다면! 이것을 가능케 해주는 것이 데이터베이스(Database, 이하 DB)이다. DB는 자바 코드가 아니라 Query문을 통해 다룬다. 여기에서는 MySQL을 사용했다.
Query
다음 네 가지는 DB를 다루는 가장 기본적인 문법으로, ‘‘로 둘러쌓인 변수는 해당 타입의 이름에 해당된다.
생성
-
create database 'db'; -
create table 'table' ('column1' 'type1', 'column2' 'type2', ...);
조회
-
select * from 'table'; -
select 'column1, column2, ...' from 'table';
수정
update 'table' set 'column' where 'condition';
삭제
delete from 'table' where 'condition';
JDBC를 이용하여 SQL을 MySQL에 요청하는 방법
1. Connection 획득
public class MySQLConnector {
private final String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test?useSSL=false&serverTimezone=UTC&allowPublicKeyRetrieval=true";
private final String id = "root";
private final String pw = "1234";
public MySQLConnector() {
}
public Connection getConnection() {
Connection conn = null;
try {
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, id, pw);
System.out.println("MySQL connect : SUCCESS!");
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return conn;
}
}
2. Statement 객체 생성 : 쿼리 내부에 변수가 포함되지 않는 경우
- 반드시 현재 접속되어 있는 Connection 객체를 통해 생성
Statement stmt = conn.createStatement();
ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery("select * from member");
int n = stmt.executeUpdate("insert into member values(1, 'ssss')");
int n = stmt.executeUpdate("update member set id=3 where name='kdh'");
int n = stmt.executeUpdate("delete from member where id=3"); // n : 변경된 쿼리의 개수
3. PreparedStatement 객체 생성 : 쿼리 내부에 변수가 포함되는 경우
- PreparedStatement pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(“쿼리”);
int idx = 3;
String name = "kdh";
String query = "insert into member values(?, ?)";
PreparedStatement pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(query);
pstmt.setInt(1, idx); // 첫번째 ?에 idx를 대입
pstmt.setString(2, name); // 두번째 ?에 name을 대입
ResultSet rs = pstmt.executeQuery();
int n = pstmt.executeUpdate();
ex) 다음은 Statement 객체를 이용하여 전체 데이터를 조회하는 코드이다.
public void selectAll() {
String query = "select * from member";
Connection conn = getConnection();
Statement stmt = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
stmt = conn.createStatement();
rs = stmt.executeQuery(query);
while (rs.next()) {
System.out.println(rs.getInt("id") + "\t" + rs.getString("name"));
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
rs.close();
stmt.close();
conn.close(); // 자원 해제(try-catch 생략)
}
}
/*
output
1 a
2 b
3 c
4 d
5 e
6 f
7 g
8 h
9 i
10 j
*/
ex) 다음은 PreparedStatement 객체를 이용하여 하나의 데이터를 조회하는 코드이다. 자원 해제를 간편히 하기 위해 close() 메서드를 선언했다.
public void selectOne(int idx) {
Connection conn = getConnection();
PreparedStatement pstmt = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
String query = "select * from member where id=?";
try {
pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(query);
pstmt.setInt(1, idx);
rs = pstmt.executeQuery();
while (rs.next()) {
System.out.println(rs.getInt(1) + "\t" + rs.getString(2)); // Column 이름 대신에 인덱스 번호로 입력 가능
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
close(conn, pstmt, rs);
}
}
/*
output
5 e
*/
ex) 위의 내용을 참고하여 insert() 메서드를 스스로 짜보았다. 테스트 결과 insert 쿼리가 잘 나간 것 같다! 비슷한 방법으로 update, delete 메서드를 짰는데 원하는 대로 잘 수행되었다.
public void insert(int idx, String name) {
Connection conn = getConnection();
PreparedStatement pstmt = null;
String query = "insert into member values(?, ?)";
try {
pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(query);
pstmt.setInt(1, idx);
pstmt.setString(2, name);
int n = pstmt.executeUpdate();
System.out.println("INSERT SUCCESS : n=" + n);
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
close(conn, pstmt, null);
}
}
/*
output
...
9 i
10 j
11 한글
3 rara
3 rara
3 rara
*/
실습 코드
오후에는 지금까지 배운 내용을 토대로 스스로 간단한 프로그램을 하나 만드는 시간을 가졌다. 주문 사항은 프로그램 실행 시 다음과 같은 메뉴가 출력되고,
1. 전체 사원 조회 | 2. 신규 사원 추가 | 3. 전사원 급여 10% 올림 | 4. 과장 직책 사원 삭제 | 5. 작업 종료
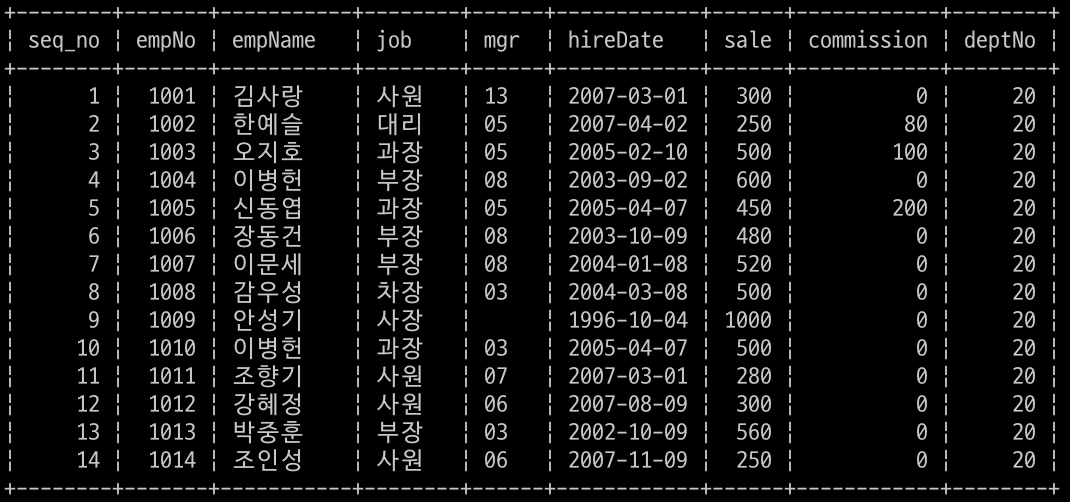
해당 번호를 입력하면 각 메뉴에 알맞는 작업이 수행되게 하는 것이다. DB의 employee 테이블에는 다음과 같이 데이터가 저장되어 있다.
Main.class
package com.chocola;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Program.start();
}
}
Program.class
package com.chocola;
import com.chocola.db.MySQLConnector;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Program {
private Program() {
}
public static void start() {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
MySQLConnector mysql = new MySQLConnector();
String menu = "1. 전체 사원 조회 | 2. 신규 사원 추가 | 3. 전사원 급여 10% 올림 | 4. 과장 직책 사원 삭제 | 5. 작업 종료";
boolean run = true;
while (run) {
System.out.println("원하는 작업 번호를 입력해주세요.\n" + menu);
System.out.print("==> ");
int input = sc.nextInt();
switch (input) {
case 1 : {
mysql.selectAll();
break;
}
case 2 : {
mysql.insert();
break;
}
case 3 : {
mysql.updateSaleAll();
break;
}
case 4 : {
mysql.deleteGwajang();
break;
}
default : {
System.out.println("프로그램을 종료합니다.");
run = false;
break;
}
}
}
}
}
main 메서드가 실행되면 콘솔에 메뉴가 나오고, 유저가 원하는 메뉴를 선택하도록 코드를 짰다. 이제 각 메뉴별로 실행되는 메서드들을 작성하면 된다.
MySQLConnector.class
DB와 연결되어 SQL을 처리하는 메서드는 MySQLConnector 클래스에 일임했다. 기본적으로 모든 SQL 처리 메서드에서 활용할 getConnection() 메서드와 close() 메서드를 정의했다.
package com.chocola.db;
import com.chocola.domain.Employee;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class MySQLConnector {
private static final String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db_emp?useSSL=false&serverTimezone=UTC&allowPublicKeyRetrieval=true";
private static final String id = "root";
private static final String pw = "1234";
private final Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
public MySQLConnector() {
}
private Connection getConnection() {
try {
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, id, pw);
System.out.println("MySQL connect : SUCCESS!");
return conn;
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
throw new IllegalStateException(e);
}
}
private void close(Connection conn, Statement stmt, ResultSet rs) {
if (rs != null) {
try {
rs.close();
System.out.println("ResultSet close");
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (stmt != null) {
try {
stmt.close();
System.out.println("Statement close");
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (conn != null) {
try {
conn.close();
System.out.println("Connection close");
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
다음은 각 메뉴에 해당하는 메서드들을 정의했다.
selectAll()
public void selectAll() {
String query = "select * from employee";
Connection conn = null;
Statement stmt = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
conn = getConnection();
stmt = conn.createStatement();
rs = stmt.executeQuery(query);
while (rs.next()) {
System.out.println(
rs.getInt("empNo") + "\t" +
rs.getString("empName") + "\t" +
rs.getString("job") + "\t" +
rs.getString("mgr") + "\t" +
rs.getString("hireDate") + "\t" +
rs.getInt("sale") + "\t" +
rs.getInt("commission") + "\t" +
rs.getInt("deptNo")
);
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
close(conn, stmt, rs);
}
}
insert()
public void insert() {
Employee employee = getEmployee();
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement pstmt = null;
String query = "insert into employee(empNo, empName, job, mgr, hireDate, sale, commission, deptNo) values(?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?)";
try {
conn = getConnection();
pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(query);
pstmt.setInt(1, employee.getEmpNo());
pstmt.setString(2, employee.getEmpName());
pstmt.setString(3, employee.getJob());
pstmt.setString(4, employee.getMgr());
pstmt.setString(5, employee.getHireDate());
pstmt.setInt(6, employee.getSale());
pstmt.setInt(7, employee.getCommission());
pstmt.setInt(8, employee.getDeptNo());
pstmt.executeUpdate();
System.out.println("INSERT SUCCESS");
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
close(conn, pstmt, null);
}
}
private Employee getEmployee() {
System.out.print("Enter empNo : ");
int empNo = sc.nextInt();
System.out.print("Enter empName : ");
String empName = sc.next();
System.out.print("Enter job : ");
String job = sc.next();
System.out.print("Enter mgr : ");
String mgr = sc.next();
System.out.print("Enter hireDate : ");
String hireDate = sc.next();
System.out.print("Enter sale : ");
int sale = sc.nextInt();
System.out.print("Enter commission : ");
int commission = sc.nextInt();
System.out.print("Enter deptNo : ");
int deptNo = sc.nextInt();
return new Employee(empNo, empName, job, mgr, hireDate, sale, commission, deptNo);
}
incrementAllSale()
public void incrementAllSale(double percent) {
Connection conn = getConnection();
PreparedStatement pstmt = null;
String query = "update employee set sale = sale * ?";
try {
pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(query);
pstmt.setDouble(1, 1 + percent / 100);
pstmt.executeUpdate();
System.out.println("UPDATE SUCCESS");
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
close(conn, pstmt, null);
}
}
delete()
public void delete(String job) {
Connection conn = getConnection();
PreparedStatement pstmt = null;
String query = "delete from employee where job = ?";
try {
pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(query);
pstmt.setString(1, job);
pstmt.executeUpdate();
System.out.println("DELETE SUCCESS");
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
close(conn, pstmt, null);
}
}
결과
selectAll()
.png)
insert()
.png)
.png)
incrementAllSale()
.png)
.png)
delete()
.png)
.png)
shutdown

느낀 점
- 이전에 이미 학습했었던 JDBC였지만 역시나 까먹은 나..!! 그래도 한 번 써봤던 경험이 있어서 기술을 적용하기 쉬웠다.
- 중복이 너무 많다고 느꼈다. 나중에 이를 해결할 기술을 배울까? 궁금했다.